Here's an explanation of the Work-Energy Theorem in 6 simple steps:
Energy:
- Energy is a property of an object that allows it to do work or cause change.
- There are different forms of energy, such as kinetic energy (energy of motion), potential energy (stored energy), and thermal energy (energy related to temperature).
Work:
- Work is done when a force is applied on an object, causing it to move.
- The amount of work done on an object is calculated by multiplying the force applied by the distance it moves in the direction of the force.
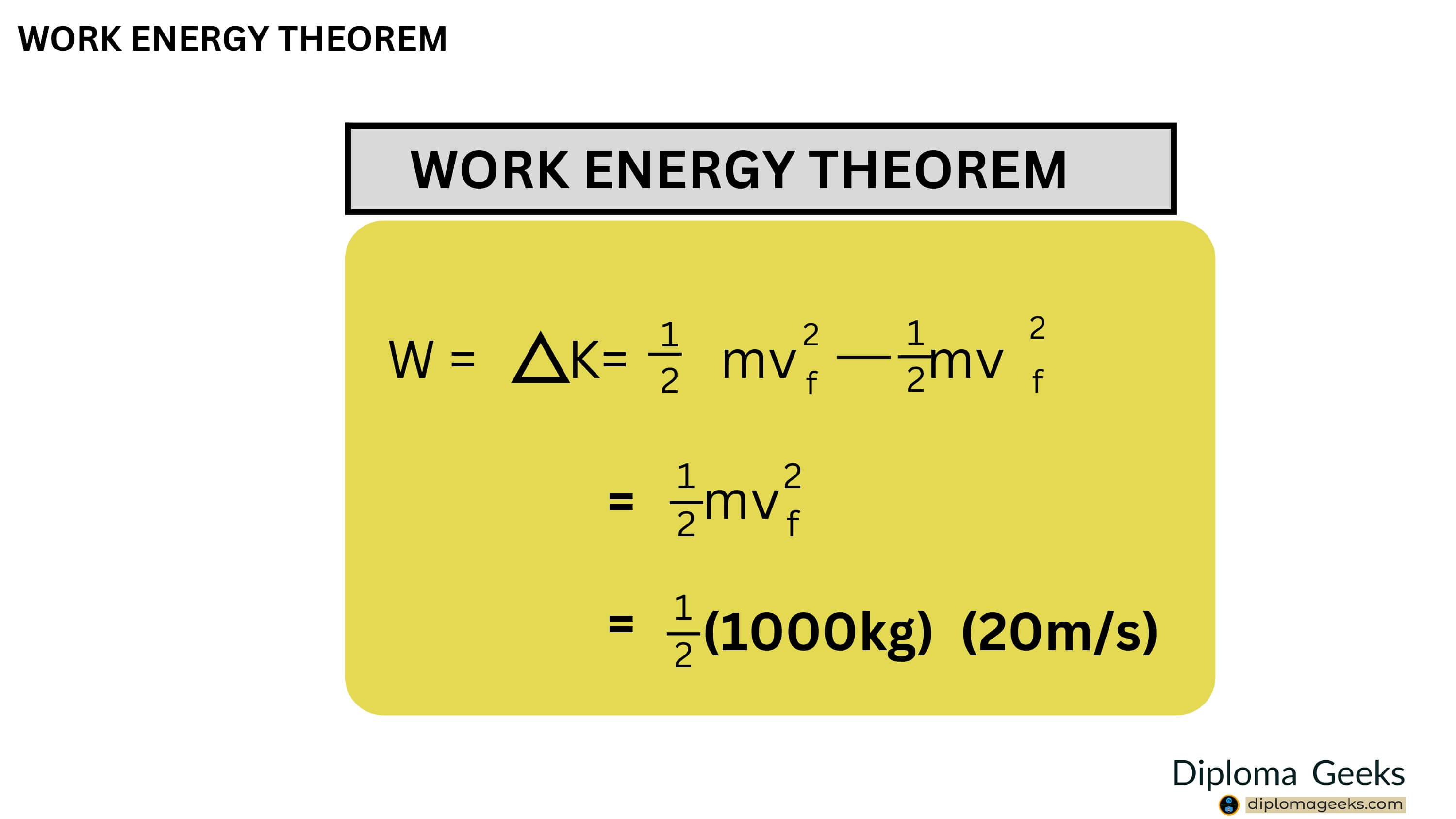
The Work-Energy Theorem:
- The Work-Energy Theorem states that the work done on an object is equal to the change in its energy.
- In other words, work and energy are interchangeable.
Example:
- For example, if you lift an object to a higher height, you are doing work on it and increasing its potential energy.
- If you then drop the object, its potential energy will be converted into kinetic energy as it falls, causing it to gain speed.
Conservation of Energy:
- The Work-Energy Theorem is related to the principle of the conservation of energy, which states that the total amount of energy in a system remains constant as long as it is not influenced by external factors.
Applications:
- The Work-Energy Theorem is used in many fields, including physics, engineering, and mechanics, to analyze and solve problems related to work and energy.
- Understanding the theorem helps us understand how energy is transformed and used in real-world applications, such as in machines, vehicles, and everyday life.